Be sure to visit our Behavior Resources webpage to better understand the process.
What is a FBA?
A functional behavioral assessment/analysis (FBA) is a process for collecting information/data to help understand why problem behaviors occur. The data will also help identify ways to address the behaviors. A FBA is then used to develop a behavior intervention plan (BIP).
How do I request a FBA?
Make your request in writing. You might want to use a sample letters as a reference.
Planning ahead for a meeting about your child’s behavior needs will help you explain your own ideas about the best way to help your child in addition to listening to the ideas of others. Once a request for an evaluation has been made, Parents can request additional evaluations be done if there are concerns that areas of need are not being identified and addressed. Under MARSE R 340.1721b, the same 30 school day timeline applies.
- More on Evaluations
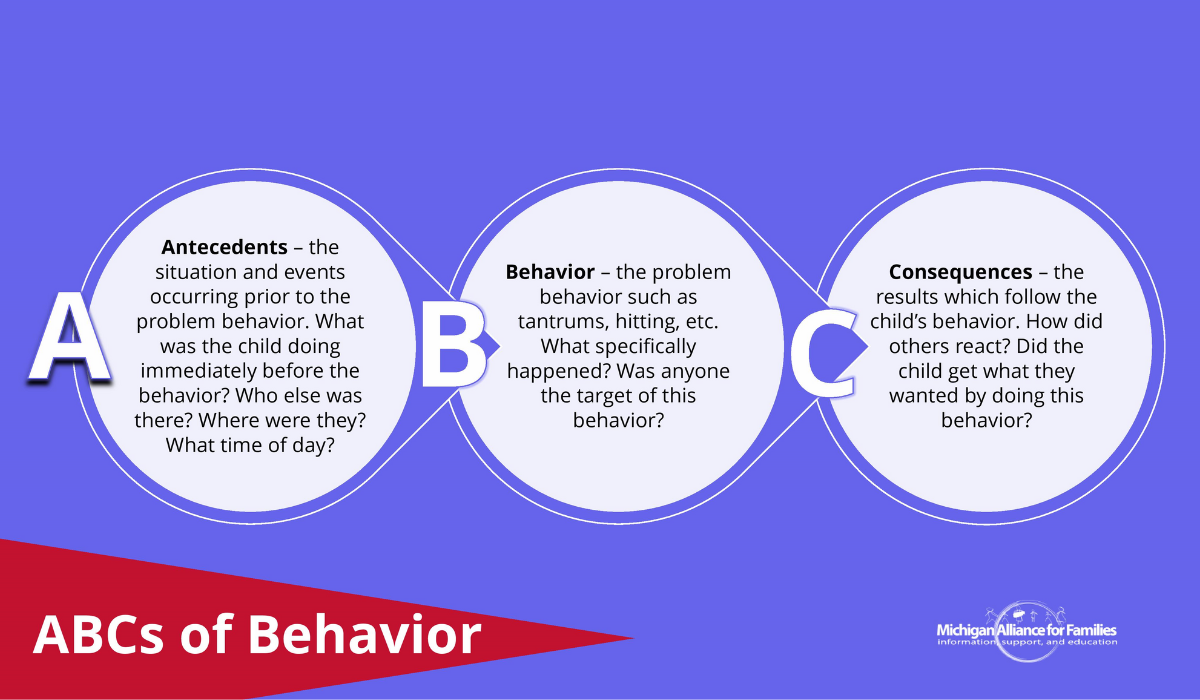
What is an ABC assessment?
This is a popular feature of many behavior assessment forms. Your school district will have a specific format they use for behavior assessment, and you can request a copy. Parents might also use the ABC technique for challenging behaviors at home.
- A is for Antecedents – the events occurring prior to the problem behavior. Often, time and location are noted in this area too. What was the child doing immediately before the behavior? Who else was there?
- B is for Behavior – the problem behavior such as tantrums, hitting, etc. A note about the intensity or duration of the behavior can be noted here. What specifically happened? Was anyone the target of this behavior?
- C is for Consequences – the consequences for the child of his behavior – the results which follow the child’s behavior (e.g., attention, power, or a correction such as time-out). How did others react? Did the child get what they wanted by doing this behavior?
Some forms include a section to mark the perceived function of the behavior, broken down into four sections:
- escape/avoidance
- get attention
- get desired object/activity
- self-stimulation
Remember that this is a best-guess as to why the behavior is occurring.
What does the law say?
You may request a FBA at any time if your child’s problem behaviors are becoming worse, or when the team cannot explain to you why the problem behaviors occur.
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) requires a FBA whenever a child with a disability has his or her current placement changed for disciplinary reasons.
The evaluation requirements of IDEA make it clear that children must be evaluated in all areas related to the suspected disability. This means that if your child has problem behaviors that are not improving, your child may need an evaluation to examine the behaviors more closely.
It is important for teams supporting students with behavioral needs, to understand the powerful role a properly conducted functional behavior assessment can have in reducing a student’s behaviors. The purpose of an FBA is to identify the function or purpose behind a student’s behavior. Understanding what may be motivating a student’s behavior, will assist districts in the development of a BIP, which when implemented with fidelity should effectively reduce or eliminate the behavior. -from Conducting a Manifestation Determination Review MDE
What do you do with the data from a FBA?
The data gathered during the FBA will be analyzed. It is important to look for any patterns or common trends, such as patterns in the days of the week, or times of the day when the problem behavior occurs. You will also want to think about when the behavior does not occur. This may give you additional clues about contributing factors.
The team should consider many factors, including:
- Is the behavior happening during the same activity and/or with the same materials?
- Does the behavior occur with specific people?
- Are there certain events/conditions that lead up to (or happen before) the behavior?
- Is there a consistent consequence?
- Does the behavior stop after a particular consequence? If this is consistent, does this mean anything about the function/ purpose of the behavior?
- Are there other personal factors that may be influencing the behavior such as illness, tiredness, or hunger?
What if I disagree with the results of the evaluation?
If you do not agree with the results of the individualized evaluation of your child, as conducted by the school system, you have the right to obtain what is known as an Independent Educational Evaluation (IEE).
Data based individual decisions require quality, tested tools – check out this chart for behavioral progress monitoring tools.
What comes after the FBA?
Once you have data, the next step is to plan for change with a Behavior Intervention Plan.
We also have a series of webpages to help understand behavior:
Accommodations/Modifications Sometimes an accommodation or modification to the classroom or the curriculum is the solution to a challenging behavior
Behavior Intervention Plan A written plan that identifies problem behaviors and how they will be addressed.
Behavior is Communication All behavior happens for a reason, but why?
Bullying Definitions, actions to take, specific protections for students with disabilities.
Discipline Covering discipline, suspension, expulsion, manifestation determination review.
Functional Behavior Assessment/Analysis A process for collecting data and analyzing the function of (ie- the reason why) a challenging behavior is occurring.
Positive Behavioral Interventions & Supports An approach to addressing challenging behaviors that teaches positive behavior skills rather than just using punishment.
Seclusion and Restraint “Seclusion” means the confinement of a pupil in a room or other space from which the pupil is physically prevented from leaving. “Restraint” means an action that prevents or significantly restricts a pupil’s movement.
Sensory Processing dysfunction can be seen as noncompliance or bad behavior.
School-Wide PBIS A building-wide initiative to support all students in school.